From chatbots that provide instant responses to self-driving cars that navigate traffic, AI is revolutionizing industries, boosting productivity by up to 40%, and driving innovation. In this article, we’ll explore what Artificial Intelligence is, how it works, and why it’s quickly becoming a game-changer for our future. Are you ready to see how AI is set to redefine our world?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a groundbreaking technology that is transforming various aspects of our daily lives. From smartphones to advanced systems in healthcare and finance, AI’s influence is growing rapidly. But what is Artificial Intelligence, and how does it impact the world around us?
At its core, Artificial Intelligence is a field within computer science focused on creating systems that perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as understanding language, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from experiences. Essentially, AI aims to develop machines and software capable of replicating human cognitive functions and improving their performance over time.
Key Aspects of AI
Machine Learning (ML)

Definition: Machine Learning is a subset of AI focused on training computers to learn from data and make predictions. Unlike traditional programming, where each step must be explicitly programmed, ML systems enhance their accuracy as they process more data.
Example: Email services use AI algorithms to filter spam. As the system encounters new spam emails, it learns to identify and block them more effectively.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)

Definition: NLP enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a meaningful way. It powers technologies such as chatbots and translation services.
Example: Chatbots like those found in customer service applications can hold conversations with users, while translation tools convert text between different languages.
Neural Networks
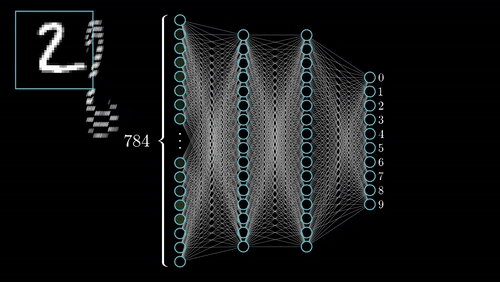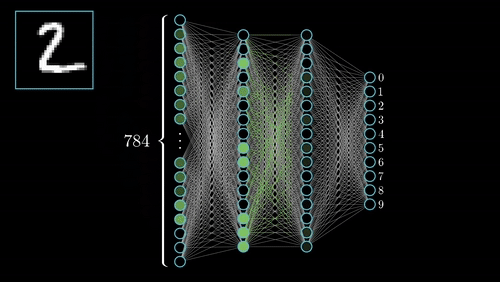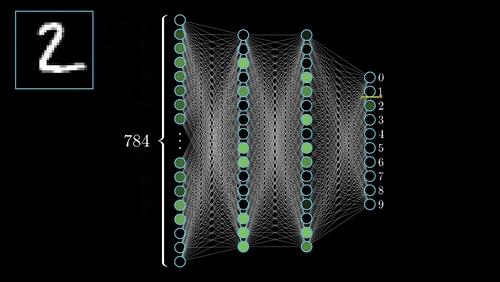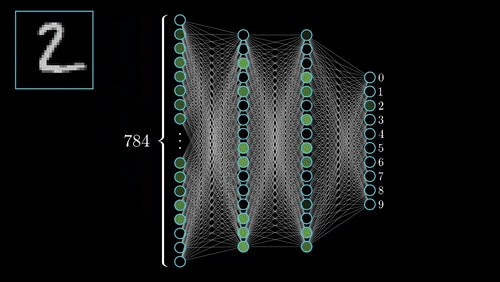
Definition: Neural Networks are inspired by the human brain’s structure. These networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process data, allowing them to recognize patterns and make decisions.
Example: Neural networks are used in image recognition systems to identify features such as faces or objects by analyzing data through multiple layers.
Robotics

Definition: Robotics involves designing robots that can perform tasks autonomously. AI-powered robots are employed in various settings, from industrial environments to domestic tasks.
Example: Robots in factories might assemble products, while home robots can perform tasks like vacuuming or lawn mowing.
Cognitive Computing

Definition: Cognitive Computing aims to mimic human thought processes, allowing machines to understand and reason about complex data. This area of AI is used in applications like medical diagnostics.
Example: Cognitive computing systems can analyze medical data to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions and recommending treatments.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of AI, we gain insight into its transformative potential and its impact on various domains. AI is not just a technological advancement but a significant shift in how we interact with and leverage technology to enhance our daily lives and solve complex problems.
Types of AI
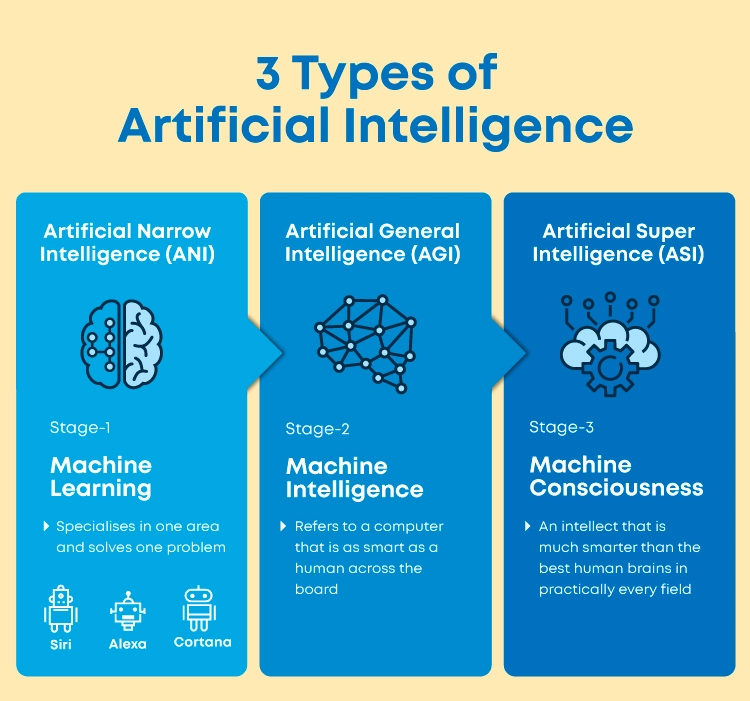
AI can be categorized based on its capabilities and the complexity of tasks it can handle. Here are the three main types of artificial intelligence:
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
- Definition: Narrow AI, often referred to as Weak AI, includes systems designed to perform a specific task or a set of related tasks. These systems operate within a narrow range of functions and cannot handle tasks beyond their design.
- Examples:
- Virtual Assistants: Siri and Alexa are examples of Narrow AI, as they help with tasks like setting reminders and answering questions but cannot engage in general human-like conversation.
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix employs Narrow AI to suggest movies based on your viewing history.
- Spam Filters: Many email systems use Narrow AI to detect and filter out spam messages.
General AI (Strong AI)
- Definition: General AI, or Strong AI, represents a more advanced form of artificial intelligence. It aims to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a broad range of tasks, similar to human cognitive abilities. This type of AI is capable of generalizing knowledge and adapting to new situations.
- Current Status: General AI remains largely theoretical and has not yet been realized. It is a significant objective for researchers and developers in the field of AI.
Artificial Superintelligence
- Definition: Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is a hypothetical form of AI that would surpass human intelligence in all areas, including creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. This level of AI is still largely speculative and not yet a reality.
- Current Status: ASI is a theoretical concept and continues to be a topic of debate and exploration.
How AI Works
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a marvel of modern technology, revolutionizing how we interact with the world. To truly understand AI’s capabilities and answer the question, What is Artificial Intelligence and how does it work?, it’s essential to grasp its core components, including algorithms, data, machine learning, and neural networks.
Algorithms and Data

Algorithms form the blueprint of AI. Imagine an algorithm as a set of instructions or rules that tells a computer how to solve a problem or perform a task. For example, Google’s search engine employs algorithms to sift through billions of web pages, evaluating various factors to deliver the most relevant results.
Data is the lifeblood of AI. It’s the information that AI systems use to learn and make decisions. Without data, AI would be ineffective, akin to a chef without ingredients. For instance, OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, a leading example of advanced AI, was trained on a vast dataset containing billions of words, allowing it to generate contextually appropriate responses across a wide range of topics.
Machine Learning
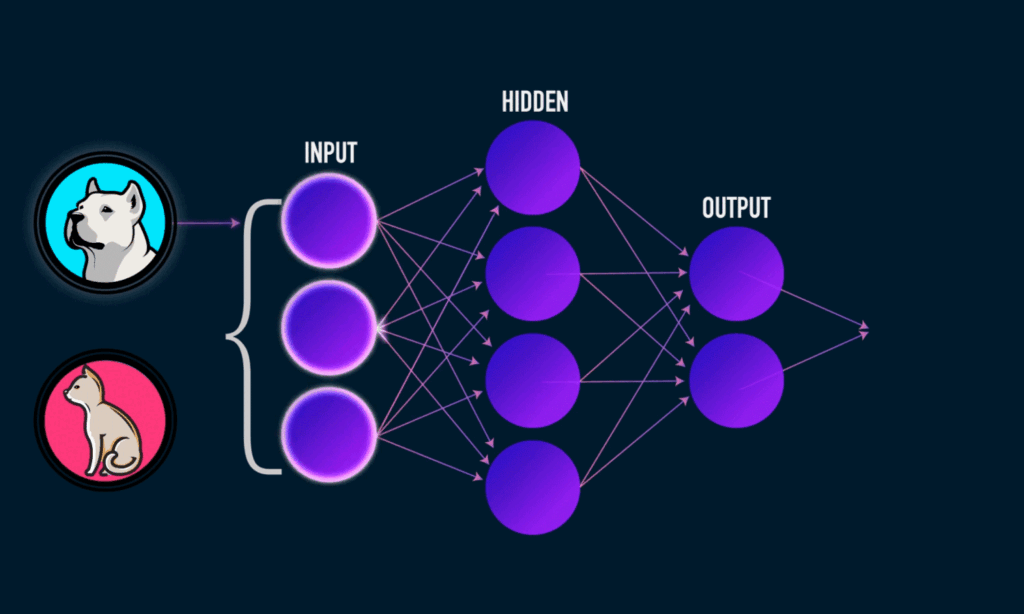
Machine Learning (ML), a key subset of AI, enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task. In supervised learning, AI models are trained on labeled data to predict outcomes based on examples. For example, spam filters use supervised learning to identify and filter out unwanted emails.
Unsupervised learning involves analyzing data without predefined labels to uncover hidden patterns. For instance, Amazon uses unsupervised learning to segment customers based on purchasing behaviors, allowing for personalized recommendations.
Reinforcement learning trains AI systems through trial and error, adjusting strategies based on feedback. For example, AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, used reinforcement learning to master the game of Go, demonstrating AI’s potential in complex decision-making.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning

Neural Networks, inspired by the human brain, consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process data through multiple layers. This architecture allows neural networks to learn and identify complex patterns. For example, facial recognition systems use neural networks to analyze images and identify individuals based on features like eyes and nose.
Deep Learning is a more advanced form of ML that employs neural networks with many hidden layers to extract intricate patterns from large datasets. For example, deep learning powers speech recognition systems in virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, enabling natural interactions through text conversion and understanding.
In autonomous vehicles, deep learning algorithms process data from various sensors to navigate and make real-time driving decisions, enhancing road safety and efficiency.
Read More
- The Ultimate Guide to Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs)
- What is Deep Learning? The Definitive Game-Changing Guide for 2024
- What Is Generative AI and How It Revolutionizes Technology
- 7 Powerful Innovations of AI in Healthcare Transforming Patient Care
- 250+ Essential ChatGPT Prompts to Dominate Any Task
- AI in Logistics: 8 Innovative Use Cases Enhancing Efficiency
- Impact of AI in Education 2024
- AI in E-Commerce: How Does It Revolutionize Shopping?
- Curious About the Best AI Coding Assistants in 2024?
Applications of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force across various domains, enhancing daily experiences and revolutionizing industries. Here are some of the most notable applications of AI in both everyday life and industrial contexts:
Everyday Applications
Personal Assistants

AI systems designed to understand and respond to voice commands for efficient task management.
- Real-World Use: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant in smartphones and smart home devices facilitate hands-free management of tasks.
- Example: Siri can set reminders, provide weather updates, or play specific songs based on voice commands.
Recommendation Systems
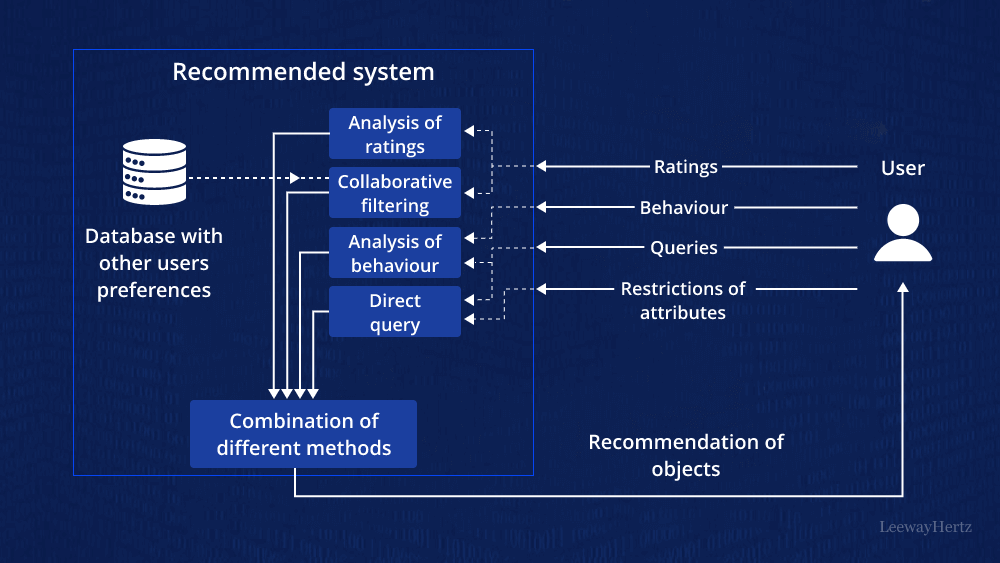
AI algorithms analyze user data to provide personalized content suggestions.
- Real-World Use: Streaming platforms and e-commerce sites use AI to recommend products or content based on user behavior.
- Example: Netflix suggests movies and shows tailored to your viewing habits.
Smart Home Devices
AI-powered gadgets learn user habits to optimize home settings and security.
- Real-World Use: Smart thermostats and security systems automatically adjust to improve comfort and safety.
- Example: Nest thermostats adapt to your daily schedule, conserving energy and maintaining comfort.
Industry Applications
Healthcare
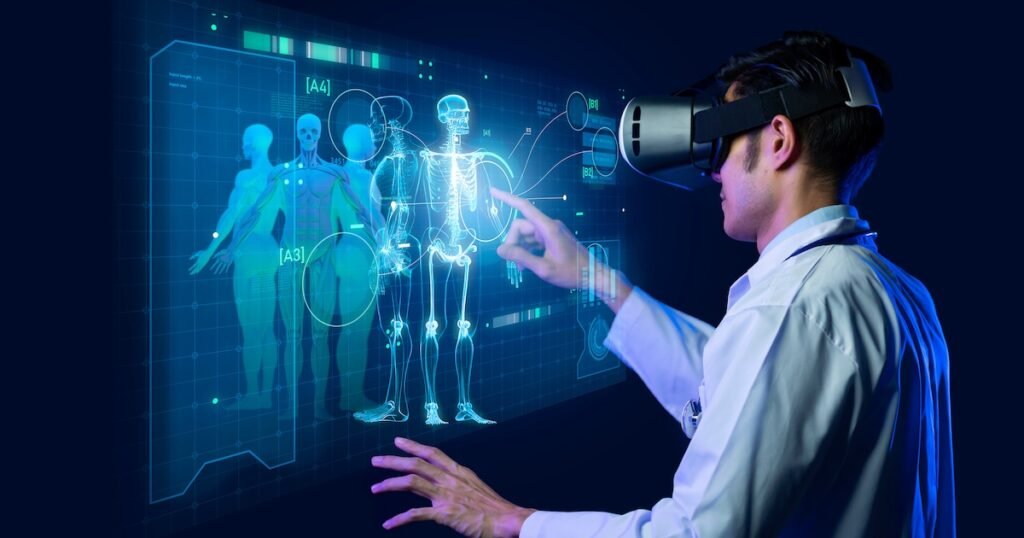

AI aids in diagnosing diseases, personalizing treatments, and managing medical data.
- Real-World Use: AI tools analyze medical images and data for more accurate diagnostics.
- Example: AI algorithms detect early signs of tumors in MRI scans, supporting timely and precise treatment.
Finance

AI enhances fraud detection, risk management, and trading strategies.
- Real-World Use: Financial institutions utilize AI to monitor transactions for fraud and analyze market trends.
- Example: AI identifies unusual spending patterns and alerts banks to potential fraud, enhancing security.
Manufacturing
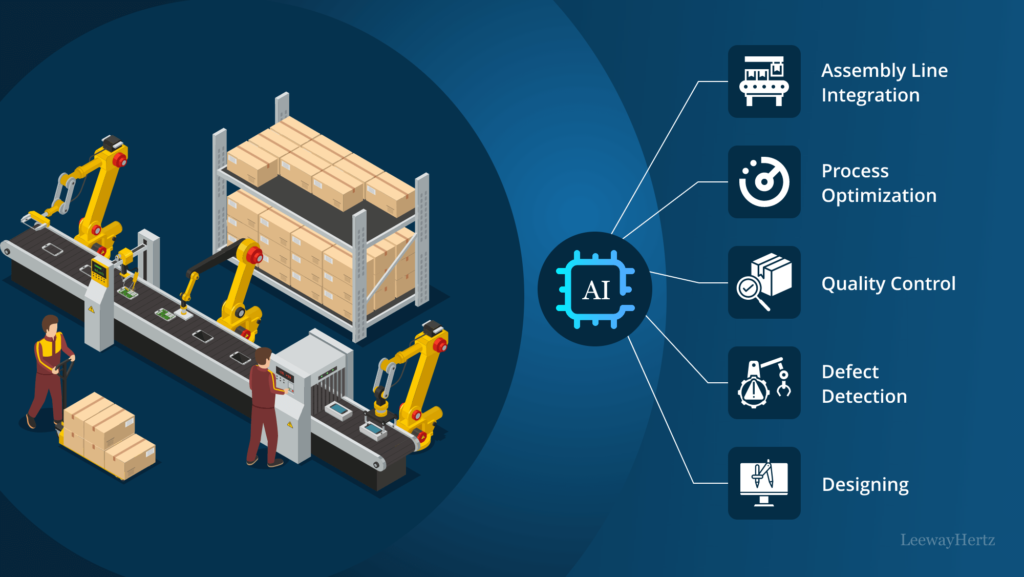
AI improves production efficiency, safety, and predictive maintenance.
- Real-World Use: Robots and predictive maintenance tools optimize production and prevent equipment failures.
- Example: Predictive maintenance forecasts machinery part replacements, reducing downtime and costs.
AI in Action: Real-World Examples
Example: Tesla’s AI technology enables autonomous navigation, obstacle avoidance, and adherence to traffic rules.
Chatbots
AI-driven chatbots automate responses to customer queries, improving service efficiency.
Real-World Use : Deployed by companies on websites or customer service platforms to handle frequent inquiries.
Example: Sephora’s chatbot provides product recommendations and order tracking, enhancing customer experience.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars use AI to navigate and make decisions, aiming for safer and more efficient transportation.
Real-World Use : AI processes data from sensors and cameras for real-time decision-making on the road.
Challenges and Limitations of AI

Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers many advantages, but it also comes with significant challenges and limitations. Here are some of the key issues that need to be addressed to ensure AI’s responsible and effective use:
Data Privacy and Security

- Challenge: AI systems often handle sensitive information, creating risks related to data breaches and misuse.
- Impact: Ensuring robust data security measures is crucial to protect personal information.
- Example: AI used in healthcare must comply with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to safeguard patient data from unauthorized access.
Bias and Fairness

- Challenge: AI algorithms can reflect biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Impact: Identifying and mitigating biases is essential to ensure equitable decision-making processes.
- Example: AI-driven recruitment tools must be designed to avoid biases based on gender, ethnicity, or age to evaluate all candidates fairly.
Ethical Considerations
- Challenge: AI deployment raises ethical questions about its impact on society and individual rights.
- Impact: Developing comprehensive ethical guidelines is necessary to ensure responsible use.
- Example: For autonomous weapons, setting ethical standards is crucial to prevent misuse and unintended harmful consequences.
Technical Limitations
- Challenge: Current AI technologies have limitations that affect their performance in complex tasks.
- Impact: Overcoming technical barriers, such as processing unstructured data, is essential for advancing AI capabilities.
- Example: Enhancing AI’s natural language understanding can improve applications like sentiment analysis and contextual comprehension.
Explainable AI (XAI)

- Importance: Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make AI’s decision-making transparent and understandable to humans.
- Challenge: Balancing transparency with the complexity of AI models is difficult; methods are needed to explain AI decisions without compromising performance.
- Example: In healthcare, explainable AI can provide clear justifications for diagnostic recommendations, building trust with medical professionals and patients.
Addressing AI’s Challenges and Limitations
To ensure AI is used responsibly, it’s crucial to focus on:
- Data Privacy: Implementing strong security protocols to protect personal data.
- Bias Mitigation: Designing AI systems to recognize and reduce bias in decision-making.
- Ethical Standards: Developing guidelines to guide the ethical use of AI technologies.
- Technical Advancements: Overcoming current technical barriers to improve AI’s capabilities.
- Transparency: Promoting explainable AI to enhance trust and accountability.
By addressing these challenges, AI can be developed and deployed in a way that maximizes its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Future of AI

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to bring transformative changes to many aspects of our lives. Here’s a simplified overview of the key trends and developments that will shape the future of AI:
Next-Gen AI: Advanced Technologies and Applications
- Quantum Computing:
- Utilizes quantum bits (qubits) for faster computations, solving problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
- Impact: Revolutionizes fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization.
- Example: Enhances AI’s ability to analyze large datasets quickly, aiding personalized medicine and scientific research.
- Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms:
- Innovations like reinforcement and transfer learning improve AI’s efficiency and adaptability with fewer examples.
- Impact: Makes AI more precise and versatile across diverse applications.
- Example: Powers breakthroughs in autonomous driving and robotics through enhanced decision-making.
- Neuromorphic Computing:
- Mimics human brain architecture for more efficient and adaptive AI systems.
- Impact: Creates energy-efficient AI with improved real-time data processing.
- Example: Boosts performance in wearable tech and smart devices.
Advanced Applications
- AI in Healthcare:
- Enhances diagnostics, personalized treatments, and drug discovery.
- Impact: Improves patient outcomes and streamlines medical research.
- Example: Enables early disease detection and more accurate treatment plans.
- AI in Autonomous Systems:
- Leads to fully autonomous vehicles, drones, and robots.
- Impact: Transforms industries by increasing efficiency and reducing human oversight.
- Example: Self-driving cars enhance road safety and transportation efficiency.
Potential Future Developments
- Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration:
- Augmented Intelligence: AI systems complement human capabilities rather than replace them.
- Impact: Supports creative tasks and strategic planning, enabling more innovative solutions.
- Example: AI assists in writing, design, and automates repetitive tasks.
- AI-Driven Innovations:
- Drives advancements in fields like space exploration and environmental conservation.
- Impact: Leads to significant discoveries and solutions for global challenges.
- Example: Analyzes satellite data for climate monitoring and disaster prediction.
General AI and Ethical Considerations
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI):
- Aims to create AI with general cognitive abilities, similar to human intelligence.
- Impact: Automates complex reasoning and decision-making, transforming industries.
- Example: AGI could perform tasks like legal analysis or advanced scientific research.
- Ethical and Societal Implications:
- Address ethical concerns to ensure AI aligns with human values.
- Impact: Develop frameworks for responsible AI use to mitigate risks.
- Example: Set standards for transparency and fairness in AI applications to maintain public trust.
The future of AI holds exciting possibilities for technological advancements and societal benefits. By focusing on innovation, human-AI collaboration, and ethical deployment, we can unlock AI’s full potential while ensuring its responsible integration into our world.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming our world, making everyday tasks easier and unlocking new possibilities across various fields. Imagine a future where AI helps us stay healthier and travel more safely—it’s closer than we think!
Yet, with such exciting advancements come important questions. As AI continues to evolve, how do we ensure it benefits everyone fairly and respects our privacy?
I’m curious about what you think! What part of AI excites or worries you the most? Drop a comment below and let’s start a conversation about how we can shape the future of AI together.





Real Estate You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Teşvikiye su kaçak tespiti Su kaçağı tespiti konusunda bu kadar etkili bir çözüm beklemiyordum. https://leenkup.com/ustaelektrikci
Büyükçekmece su kaçağı tespiti Yerel Bir Firma: Mahallemizde bu kadar kaliteli bir hizmet almak şaşırtıcıydı. https://faithbudy.com/ustaelektrikci
You have brought up a very good points, thanks for the post.
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I have discovered till now. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
great post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You should continue your writing. I’m sure, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
You are my breathing in, I possess few blogs and occasionally run out from to post .
My husband and i felt very joyous John managed to conclude his preliminary research by way of the ideas he got using your web page. It’s not at all simplistic just to happen to be making a gift of secrets and techniques that the rest may have been trying to sell. Therefore we know we need you to be grateful to because of that. These illustrations you have made, the straightforward blog menu, the friendships your site give support to foster – it’s everything wonderful, and it’s helping our son in addition to our family feel that this concept is satisfying, and that is tremendously indispensable. Thank you for everything!