What is Business? It’s more than just buying and selling; it’s a driving force in our society. Businesses create jobs, spark innovation, and shape our world. But beyond the profits, businesses have a responsibility to do the right thing. By being ethical, sustainable, and inclusive, companies can not only improve their reputation but also make a positive impact on our world. Let’s explore how businesses can harness their power for good and build a better future together.
Brief Overview of Business
Consider the everyday products and services that simplify our lives. From the local bakery that offers fresh bread with a friendly smile to the tech giant that keeps us connected globally, businesses are at the heart of these experiences. But what is business truly about? It’s more than just transactions—it’s about creating value and addressing needs.
Take Apple, for example. Apple turns cutting-edge technology into sleek, user-friendly devices like the iPhone and MacBook. Through innovation and design, it enhances user experiences and drives industry trends. Amazon, on the other hand, has transformed the shopping experience by providing a vast array of products delivered directly to consumers’ doors. Its efficient logistics and extensive product range illustrate how businesses can redefine convenience and accessibility.
Importance of Understanding What is Business

Grasping the essence of “What is business?” offers several key benefits:
- For Entrepreneurs: Comprehending business fundamentals is crucial when launching a new venture. For instance, examining how companies like Tesla have revolutionized the automotive industry with their electric vehicles can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own entrepreneurial journey.
- For Consumers: Understanding how businesses operate allows you to make more informed choices. For example, knowing how Starbucks sources its coffee beans and manages its global operations helps you appreciate the company’s value proposition and ethical practices.
- For Professionals: Knowledge of business principles enhances strategic thinking across various careers. Learning from how Microsoft manages its extensive portfolio and global operations can refine your own professional strategies and decision-making processes.
Overall, a clear understanding of “What is business?” enriches both personal and professional aspects of life, providing valuable perspectives on how businesses operate and succeed.
What is a Business?

At its core, a business is an organized effort to create and deliver products or services with the primary aim of earning a profit. This structured approach encompasses various aspects, from production to sales, and involves intricate planning and execution to achieve financial success. Let’s explore how different businesses exemplify this concept:
- Nike: Designs and markets sportswear and equipment globally, utilizing a sophisticated supply chain and marketing strategy to cater to customer needs and drive sales.
- Walmart: Manages a vast network of retail stores and an extensive online platform, providing a diverse range of products at competitive prices through an efficient logistics system.
Key Characteristics of a Business
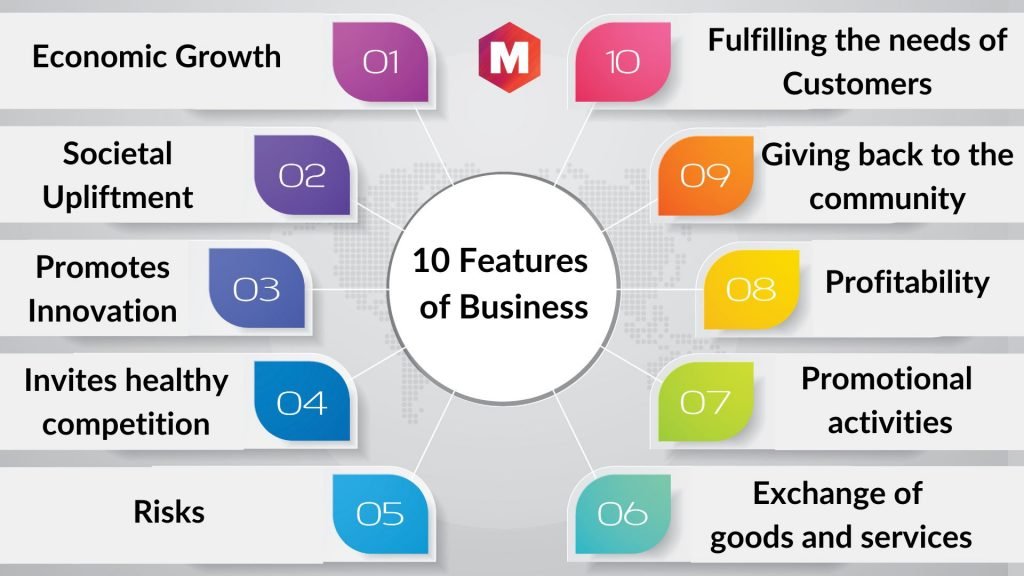
Understanding “What is business?” involves examining its key characteristics. Here’s a closer look at these characteristics with real-world examples:
Organized Effort

A business is structured to efficiently manage its operations and resources:
- Google: Organizes its efforts around its search engine, advertising platforms, and cloud services. Its well-defined structure ensures streamlined operations and continuous innovation.
- McDonald’s: Utilizes a standardized approach to provide consistent fast food experiences globally. The company has clear roles and processes across its franchises to ensure uniformity and efficiency.
Value Creation
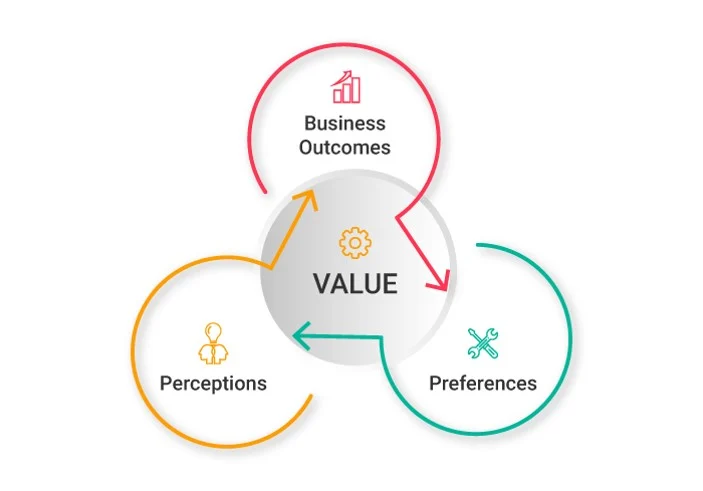
Businesses create value by offering products or services that meet customer needs and preferences:
- Apple: Adds value through its innovative technology products, such as the iPhone and MacBook, enhancing user experiences with cutting-edge design and functionality.
- Amazon: Provides value by offering an extensive product selection, convenience, and rapid delivery services, reshaping the retail landscape with its comprehensive online platform.
Profit Motive

The pursuit of profit drives business strategies and decisions:
- Tesla: Aims to achieve profitability by producing and selling electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions. Its focus on innovation helps capture market share and drive financial growth.
- Coca-Cola: Generates profit through its extensive beverage portfolio and global distribution network, continuously expanding its market presence and optimizing its product offerings.
Exchange Mechanism
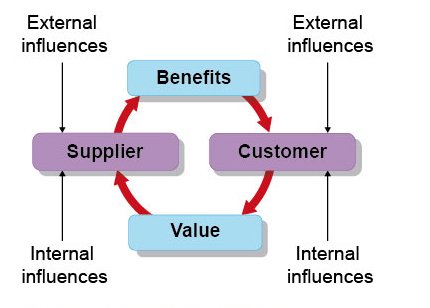
Businesses facilitate exchanges of goods or services for monetary value:
- eBay: Operates an online marketplace that connects buyers and sellers, earning revenue from transaction fees and facilitating global commerce.
- Netflix: Provides a subscription-based streaming service, exchanging digital content for recurring payments from users, and continually expanding its media library to retain subscribers.
Risk and Reward

Business ventures involve risks but also offer potential rewards:
- SpaceX: Takes significant risks in developing advanced space technologies with the potential for substantial rewards in space exploration and commercial success.
- Uber: Navigates regulatory challenges and competitive pressures with the goal of transforming urban transportation and achieving global expansion.
These characteristics, exemplified through various enterprises, help clarify what constitutes a business and how different models and strategies contribute to its success and impact. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insights into the diverse world of business operations and objectives.
Types of Businesses
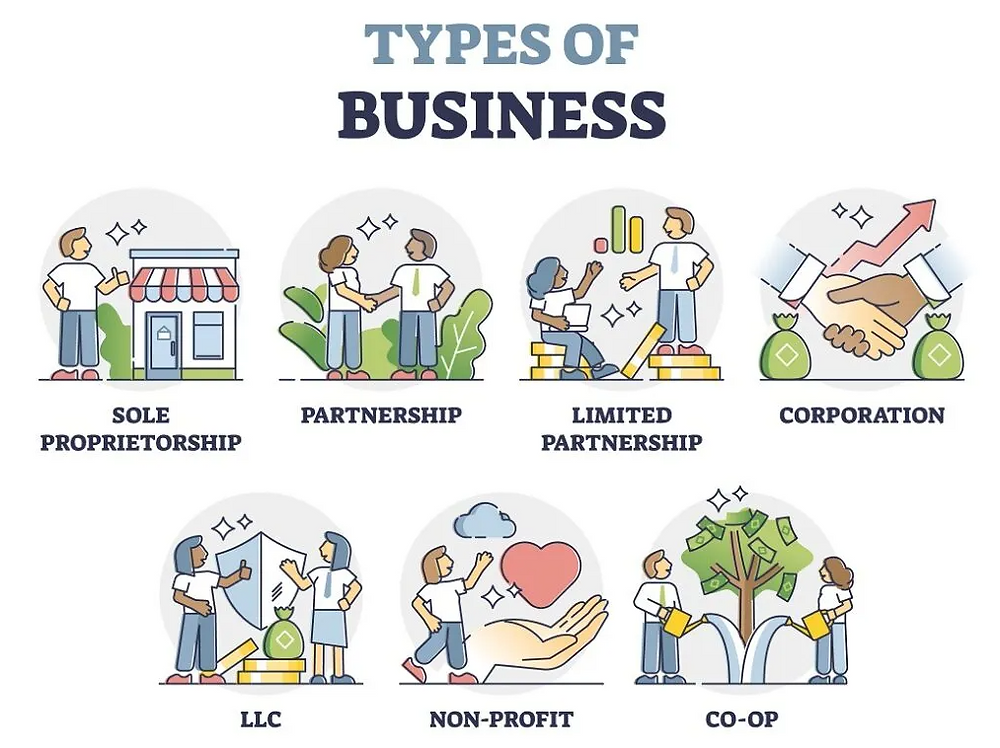
Understanding the different types of businesses helps clarify how they operate and what differentiates them from each other. This section explores key business categories and models, offering clear examples to provide a comprehensive overview.
Profit Businesses

Profit Businesses are designed to generate revenue that exceeds their expenses, aiming to deliver profits to their owners or shareholders. They are driven by market demand, competition, and the goal of financial growth.
- Walmart: A prime example of a for-profit business. Operating retail stores globally, Walmart aims to generate profit by offering a wide range of products at competitive prices. The company focuses on efficiency and cost management to ensure its revenue exceeds operational costs.
Non-Profit Organizations

Non-Profit Organizations focus on addressing social, environmental, or community issues rather than generating profit. Any surplus funds are reinvested into their mission to support and advance their cause. Non-profits typically rely on donations, grants, and volunteers.
- The Red Cross: A notable non-profit organization dedicated to humanitarian aid and disaster relief. It relies on donations and grants to fund its operations and support affected communities. The surplus funds are used to further its mission rather than being distributed as profit.
Sole Proprietorship

Sole Proprietorship is the simplest form of business structure, where a single individual owns and operates the business. This owner is personally responsible for all aspects of the business, including profits, losses, and liabilities.
- Example: A freelance graphic designer operates as a sole proprietorship. They handle all aspects of their business independently, from managing client relationships to financial management. All profits and risks are solely theirs.
Partnership
Partnership involves two or more individuals who share ownership and responsibilities. Partnerships can be general, where all partners are involved in managing the business and share liability, or limited, where some partners have limited involvement and liability.
- Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom LLP: A law firm structured as a partnership. The firm comprises multiple attorneys who share management responsibilities and profits. Each partner contributes their expertise and shares in both the successes and challenges of the firm.
LLC (Limited Liability Company)

LLC (Limited Liability Company) combines features of both partnerships and corporations. It offers limited liability protection to its owners while allowing flexible management and tax benefits. LLCs are often preferred for their simplicity and protection.
- Example: Ben & Jerry’s operates as an LLC, combining operational flexibility with the advantage of limited liability for its owners. This structure supports its unique business approach and social mission.
Corporation

Corporation is a more complex structure where the business is a separate legal entity from its owners. Corporations provide limited liability protection to their owners and can raise capital by issuing shares. They are governed by a board of directors and are subject to specific regulatory requirements.
- Zoom Video Communications: An example of a corporation. It has shareholders and a board of directors and can raise capital through stock offerings. As a corporation, Zoom benefits from limited liability protection and possesses the flexibility to expand and innovate.
By understanding these business types, you gain insight into various business models and the fundamental business definitions that guide how companies operate and achieve their objectives. Whether through for-profit strategies or non-profit missions, and across different structures like sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, each type has its unique approach to creating and delivering value.
Business Models
Business models outline how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. They are essential for understanding how businesses operate and generate revenue. Each model represents a unique approach to structuring operations and achieving success.
Product-Based Models
Product-Based Models involve companies that focus on producing and selling physical goods. These businesses center their operations around manufacturing, distributing, and selling tangible products.
Example: Apple Inc. is a prominent example of a product-based model. The company designs, manufactures, and sells a variety of consumer electronics, such as iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks. Apple’s business model is characterized by high-quality, innovative products and a premium pricing strategy. The company invests significantly in research and development to stay ahead in technology and continuously improve its product offerings.
Key Aspects:
- Production: Involves manufacturing goods or sourcing them from suppliers. Efficient production processes are crucial for maintaining product quality and cost-effectiveness.
- Distribution: Includes logistics involved in getting products from the production site to the consumer, such as warehousing, shipping, and managing supply chains.
- Sales: Strategies employed to sell products through retail and online channels. Effective sales tactics are essential for maximizing reach and revenue.
Service-Based Models

Service-Based Models focus on delivering intangible value through services rather than physical products. These businesses provide expertise, support, or experiences that address customer needs and solve problems.
Example: McKinsey & Company is a prime example of a service-based model. As a global consulting firm, McKinsey provides advisory services across various sectors. The firm’s revenue comes from consulting fees for strategic advice, operational improvements, and management solutions. McKinsey’s reputation and expertise help attract and retain high-profile clients.
Key Aspects:
- Expertise: Providing specialized knowledge or skills that address specific client needs, often involving high-level consulting or professional services.
- Client Relationship: Building and maintaining strong relationships with clients to ensure satisfaction and foster repeat business.
- Service Delivery: Methods for delivering services, such as in-person consultations, remote assistance, or tailored solutions. High-quality service delivery is crucial for client retention.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid Models combine elements of both product and service-based approaches. These businesses offer physical products along with related services, creating a more comprehensive value proposition.
Example: Amazon is a notable example of a hybrid model. The company operates an extensive e-commerce platform for selling a broad range of products, from electronics to clothing. Additionally, Amazon provides services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), which offers cloud computing and data storage solutions. This hybrid approach allows Amazon to diversify its revenue streams and meet various customer needs effectively.
Key Aspects:
- Product Offering: Selling physical goods to consumers, including managing inventory, marketing products, and fulfilling orders.
- Service Offering: Providing additional services such as customer support, subscription plans, or technological solutions. These services complement the product offerings and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Integration: Combining product and service elements to create a more comprehensive value proposition. This integration can lead to increased customer loyalty and additional revenue opportunities.
Understanding these business models helps in comprehending the broader concept of what is business and how different companies approach value creation. Whether through product-based, service-based, or hybrid models, each approach has its unique strategies and operational methods tailored to its specific market and objectives.
Business Objectives

Business objectives define what a company aims to achieve and guide its strategic direction. Understanding these objectives is crucial in comprehending what is business and how companies navigate toward success. Clear and well-defined objectives help align efforts across the organization and provide measurable benchmarks for success.
Profit Maximization

Profit Maximization involves strategies aimed at increasing a company’s financial returns. This objective is central to many business models, where the primary goal is to optimize pricing, reduce costs, and enhance revenue streams.
Example: Walmart exemplifies profit maximization through its cost leadership strategy. By leveraging its vast size and scale, Walmart negotiates lower prices with suppliers, allowing it to offer competitive pricing to consumers. Additionally, Walmart’s efficient supply chain management and operational efficiencies further contribute to its profitability.
Key Aspects:
- Cost Management: Reducing expenses to improve profit margins is fundamental to profit maximization. Companies often streamline operations and minimize costs through various business models.
- Revenue Enhancement: Strategies to increase sales, such as promotions and product diversification, play a critical role in achieving higher profits.
- Pricing Strategy: Setting prices to maximize revenue while remaining competitive is essential for sustaining long-term profitability.
Growth and Expansion

Growth and Expansion focus on increasing a company’s market presence and scaling its operations. This can involve opening new locations, entering new markets, or expanding product lines. Companies employ different strategies based on their objectives and market conditions.
Example: Subway is a prime example of growth and expansion through its global franchise model. The company has rapidly expanded by opening thousands of new locations worldwide. Subway’s franchise approach enables quick growth while leveraging local knowledge and investment from franchisees.
Key Aspects:
- Market Penetration: Increasing presence in existing markets by enhancing product offerings or improving customer engagement.
- Geographic Expansion: Entering new geographic regions or countries as a significant growth strategy.
- Product Line Expansion: Adding new products or services to the existing portfolio to diversify and reach new customer segments.
Social Impact

Social Impact refers to a company’s efforts to make a positive contribution to society through its business practices. Companies increasingly focus on sustainability, ethical practices, and community engagement as part of their business objectives.
Example: Patagonia, a certified B Corporation, prioritizes social impact by integrating sustainability into its business model. The company uses recycled materials, supports environmental initiatives, and maintains fair labor practices. Patagonia’s commitment to social responsibility enhances its brand reputation and attracts environmentally conscious consumers.
Key Aspects:
- Sustainability: Implementing eco-friendly practices and reducing environmental impact is a growing priority for many companies, particularly in industries tied to environmental resources.
- Ethical Practices: Ensuring fair labor practices and ethical sourcing is essential for maintaining a positive brand image and building consumer trust.
- Community Engagement: Supporting local communities and social causes helps build strong relationships with stakeholders and contribute to societal well-being.
Understanding these business objectives provides insight into how companies operate and strive to achieve their goals. Whether focusing on profit maximization, growth and expansion, or social impact, these objectives shape the strategies and practices that drive business success.
Key Functions of Business

Understanding the key functions of a business is essential to grasp the broader concept of what is business. These functions—marketing, finance, and operations—are integral to the success of any business model. Each function plays a unique role in supporting overall operations and driving business objectives.
Marketing

Marketing is a fundamental function that involves activities and strategies aimed at promoting products or services, attracting customers, and ultimately driving sales. Through marketing, businesses create brand awareness, engage with consumers, and generate revenue.
Example: Coca-Cola exemplifies successful brand promotion through its marketing strategies. The company’s “Share a Coke” campaign personalized the consumer experience, strengthening brand loyalty and boosting sales—a perfect case study when examining various business models.
Key Aspects:
- Market Research: Understanding customer needs, preferences, and behaviors to tailor products and marketing efforts—a crucial step in defining what is business and its target market.
- Advertising: Crafting and disseminating promotional messages through various channels, which is key in all types of business, from startups to established corporations.
- Sales Strategies: Developing approaches to convert prospects into loyal customers, which is vital in any business definition focusing on revenue generation.
Finance

Finance involves the strategic management of a company’s financial resources, encompassing budgeting, investment, and financial planning. Effective financial management is crucial for sustaining operations, investing in growth, and ensuring long-term financial stability.
Example: Google highlights the importance of resource allocation in successful business operations through its sophisticated financial management practices. From budgeting for research and development to managing cash flow, Google’s approach is a benchmark for financial excellence in the tech industry.
Key Aspects:
- Budgeting: Planning and controlling financial resources to ensure funds are allocated appropriately, reflecting the financial priorities in various types of business.
- Investment: Allocating funds to growth opportunities, such as new technologies or market expansion, aligning with the goals of different business models.
- Financial Analysis: Evaluating financial performance using metrics like ROI and profit margins, which are central to a clear business definition and strategic decision-making.
Operations

Operations focus on the day-to-day activities necessary to produce goods or deliver services. This function is critical for optimizing resources, reducing costs, and ensuring high-quality output, making it a cornerstone in understanding what is business and how different types of business operate.
Example: Toyota exemplifies efficient operations management with its Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing system. By minimizing inventory and reducing waste, Toyota improves production efficiency and maintains high-quality standards—demonstrating the impact of operational excellence on various business models.
Key Aspects:
- Production Management: Overseeing the manufacturing process to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness—a key element in any business definition focused on product-based models.
- Supply Chain Management: Coordinating the flow of materials and products from suppliers to customers, essential for all types of business, from retail to manufacturing.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products or services meet established standards, which is vital for customer satisfaction and brand reputation across different business models.
Business Environment

The business environment includes all factors that influence a company’s operations and success. These factors are divided into internal and external components, each playing a crucial role in shaping strategies and outcomes.
Internal Environment

The internal environment consists of elements within a company that directly affect its daily operations and overall culture. Key components include:
- Organizational Culture: The values, beliefs, and practices shared within a company play a significant role in shaping the work environment. A positive culture can enhance employee satisfaction, boost productivity, and drive innovation.
Example: In 2024, Google continues to set the standard for creating a dynamic work culture. With initiatives like hybrid work models and enhanced wellness programs, Google fosters an environment that attracts top talent and promotes innovation. - Resources: These are the assets a company uses, including financial, human, and physical resources. Effective management of these resources is vital for operational success and achieving long-term objectives.
Example: Microsoft invests in advanced technologies and a robust cloud infrastructure, supporting its wide range of services and helping the company stay competitive in the tech industry. - Management Practices: Leadership strategies and methods used to guide the company are crucial for reaching business goals and driving growth.
Example: Amazon uses data-driven management practices to streamline logistics and customer service operations, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
External Environment

The external environment includes factors outside a company that affect its operations and performance. These factors include economic conditions, market trends, and regulatory frameworks.
- Economic Conditions: The state of the economy, including inflation rates, employment levels, and economic growth, significantly impacts business performance.
Example: In 2024, the economic recovery post-pandemic continues to influence consumer spending. Retailers like Target adapt by improving their online shopping platforms and optimizing supply chains to meet evolving consumer demands. - Market Trends: Changes in consumer preferences and industry developments shape business strategies. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for maintaining relevance.
Example: The rise of sustainable fashion reflects a shift towards eco-friendly products. Brands like Patagonia capitalize on this trend by promoting sustainable practices and materials. - Regulatory Framework: This includes laws and regulations that businesses must comply with, covering areas like environmental standards, labor practices, and data protection.
Example: In 2024, updates to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, require companies like Facebook to enhance their data protection and transparency efforts.
Challenges in Business

Businesses face a variety of challenges that can significantly impact their success and operations. Addressing these challenges effectively is essential for maintaining competitiveness and achieving long-term goals.
Market Competition

Market Competition involves rivalry among companies offering similar products or services. Competition can drive innovation, influence pricing strategies, and impact market share.
Example: The ongoing competition between Apple and Samsung in the smartphone market drives both companies to introduce new features and adjust prices to capture market share. This competition encourages continuous innovation and keeps the market dynamic.
Key Aspects:
- Innovation: Companies must continuously innovate to stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving consumer needs.
- Pricing Strategies: Adjusting prices to remain competitive while maintaining profitability is crucial.
- Market Positioning: Differentiating products or services to stand out in a crowded market.
Economic Fluctuations

Economic Fluctuations refer to changes in the economic environment, such as recessions, inflation, and other financial conditions that can impact business performance.
Example: The economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic continue to influence small businesses in 2024. Many have adapted by offering delivery and takeout options to meet changing consumer preferences and sustain operations during uncertain economic times.
Key Aspects:
- Economic Conditions: Monitoring economic indicators to anticipate and respond to changes.
- Adaptability: Adjusting business strategies to mitigate the impact of economic fluctuations.
- Cost Management: Managing expenses effectively to maintain financial stability during economic downturns.
Regulatory Issues
Regulatory Issues involve compliance with laws and regulations, which can entail significant costs and operational adjustments. Navigating these requirements is crucial for avoiding legal issues and maintaining operational integrity.
Example: Nestlé invests in compliance with evolving food safety regulations to ensure product quality and avoid legal issues. Adhering to these regulations helps the company maintain its reputation and operational standards.
Key Aspects:
- Compliance Costs: Managing the financial impact of regulatory requirements.
- Operational Adjustments: Implementing changes to meet regulatory standards and maintain compliance.
- Legal Risks: Minimizing the risk of legal issues through diligent adherence to regulations.
Read More
- What is Deep Learning? The Definitive Game-Changing Guide for 2024
- 10 Key Insights: What Is Generative AI and How It Revolutionizes Technology
- 7 Powerful Innovations of AI in Healthcare Transforming Patient Care
- AI in Logistics: 8 Innovative Use Cases Enhancing Efficiency
- The Revolutionary Impact of AI in Education 2024: Transforming Learning and Teaching
- AI in E-Commerce: What 5 Supercharging Ways Does It Revolutionize Shopping?
- Curious About the Best AI Coding Assistants in 2024? Top 10 Revealed!
Conclusion
Understanding what is business is crucial in today’s competitive landscape. At its core, business is more than just generating profits; it involves creating value, meeting customer needs, and making a positive impact on society. Whether it’s a global leader like Apple or a local small business, the fundamental principles remain consistent: understanding market dynamics, delivering high-quality products or services, and adapting to changes.
In 2024 and beyond, businesses will continue to evolve, influenced by emerging technologies, shifting consumer preferences, and global trends. Companies that master business models and effectively manage market competition, navigate economic fluctuations, and address regulatory issues will thrive. The diverse types of businesses, from product-based models to service-based models and hybrid models, illustrate how different strategies can drive success.
Business objectives such as profit maximization, growth, and social impact are central to achieving long-term success. Understanding these objectives helps businesses align their strategies and operations with their goals. Business definition provides a framework for exploring how companies operate and succeed, whether through innovative approaches or by addressing critical challenges.
Grasping the essentials of what is business provides a solid foundation for anyone looking to excel in the business world. Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur or exploring business fundamentals, understanding these key concepts will help you navigate the complexities of the business environment effectively. Embracing these principles ensures preparedness to drive business growth, achieve financial stability, and make a meaningful impact.






Thanks for always providing such reliable and well-researched content!
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your website is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you’ve on this site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and just couldn’t come across. What a perfect web site.
It¦s really a great and helpful piece of info. I am satisfied that you just shared this useful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Spot on with this write-up, I actually assume this website wants far more consideration. I’ll probably be again to learn much more, thanks for that info.